Why exercise is key to living a long and healthy life
Research shows there are a few lifestyle interventions that can effectively prolong our life and health span. One of these is exercise, but what kind, and in what combinations, and why does it help add years to our lives? Find out in our latest podcast episode.
Seemingly since times immemorial, humankind has been, metaphorically speaking, seeking the path that leads to the “Fountain of Youth” — that is ways to ensure a longer, healthier life.
And while we may not yet benefit of any “miracle” medicines or technologies to prolong our life spans well over the hundred-year mark, many recent studies have provided strong evidence in support of the notion that simple, achievable lifestyle changes can help us stay healthy for longer and decrease our risk of premature death.
Research presented at the American Heart Association’s Scientific Sessions 2023, for example, suggested that eight healthy habits can slow down biological aging by as much as 6 years.
These habits are related to diet, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding tobacco, maintaining good sleep hygiene, managing cholesterol, blood sugar, and blood pressure, and, no less importantly, staying physically active.
Dr. del Pozo Cruz is principal researcher in Applied Health Sciences at the University of Cadiz in Spain, and adjunct associate professor in the Department of Sports Science and Clinical Biomechanics at the University of Southern Denmark.
In collaboration with other researchers, Dr. del Pozo Cruz has conducted various studies exploring the link between different forms of exercise and the risk of death from different causes.
Dr. Brocklesby has gained fame under the nickname “Iron Gran,” as at the age of 72, she was the oldest British woman to complete an Ironman Triathlon.
What types of exercise lower death risk?
in August 2023, Dr. del Pozo Cruz and his colleagues analyzed data from 500,705 participants followed up for a median period of 10 years to see how different forms of exercise related to a person’s mortality risk.
The study looked at the effect of moderate aerobic physical activity, such as walking or gentle cycling, vigorous aerobic physical activity, such as running, and muscle-strengthening activity, like weight lifting.
Its findings indicated that a balanced combination of all of these forms of exercise worked best for reducing mortality risk.
More specifically, around 75 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise, plus more than 150 minutes of vigorous exercise, alongside at least a couple of strength training sessions per week were associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality.
When it came to reducing the risk of death linked to cardiovascular disease specifically, Dr. del Pozo Cruz and his collaborators suggested combining a minimum of 150–225 minutes of moderate physical activity with around 75 minutes of vigorous exercise, and two or more strength training sessions per week.
Dr. Brocklesby, who goes by “Eddie,” is herself an example of the importance of combining different forms of exercise. Indeed, training and participating in a triathlon — which is an endurance multisport race where participants compete in swimming, cycling, and running — involves achieving a balanced “diet” of moderate and vigorous exercise, as well as strength training.
How little exercise is enough?
But what about people who are not nearly as athletic? What is the minimum “amount” of exercise that could help fend off some of the conditions that pose the highest threat to health?
This research suggested that engaging in vigorous exercise for only 2 minutes a day could help slash the risk of death related to cancer or cardiovascular events.
The researchers found that study participants who never engaged in vigorous exercise had a 4% risk of dying within 5 years, but introducing less than 10 minutes of vigorous activity weekly halved this risk. Moreover, their risk of death halved again for those who engaged in at least 60 minutes of exercise per week.
“A substantially lower risk of mortality was observed among individuals who had adequate levels of both long-term leisure time moderate and vigorous physical activity”, the study says, noting that higher levels of vigorous physical activity were associated with lower mortality among those with insufficient levels of moderate physical activity each week.
But this was not the case for those who already had high levels of moderate physical activity—more than 300 minutes each week.
With that, the study notes that “any combination of medium to high levels” of vigorous (75 to 300 minutes per week) and moderate physical activity (150 to 600 minutes per week) “can provide nearly the maximum mortality reduction,” which is about 35% to 42%.
Additionally, people who are insufficiently active—meaning less than 75 minutes per week of vigorous or less than 150 minutes of moderate physical activity—could get greater benefits in mortality reduction by adding in modest levels of either exercise. This means 75 to 150 minutes per week of vigorous exercise or 150 to 300 minutes each week of moderate physical activity. Doing so can reduce mortality by 22% to 31%.
Artificial sweeteners: ‘Sweet taste in itself’ may affect metabolism
“Sweetness should be consumed in moderation, regardless of the calories,”
caution researchers, as a new study reveals the impact of consuming artificial sweeteners on metabolism and glucose control.
New research suggests that artificial sweeteners also have metabolic effects.
Lately, we have been hearing a lot in the media about the dangers of sugar consumption. Added sugar raises the risk of obesity, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes, not to mention having an addictive effect on the brain.
Therefore, in an attempt to avoid sugar, many people have turned to low calorie sweeteners instead. Artificial sweeteners provide the sweet taste with none of the side effects, so it appears to be a welcome and healthful “trick.”
So, many people have bought into the idea that, according to some estimates, about a quarter of children in the United States, and more than 40% of adults, are currently consuming low calorie sweeteners.
But, are artificial sweeteners as harmless as people seem to think? Research from a few years ago suggested that artificial sweeteners can still promote diabetes and obesity. And now, a new study adds to the evidence that sweeteners may have undeniable metabolic effects.
In fact, the latest study suggests that merely tasting something sweet could alter our metabolism and glucose control.
People should consume sweetness in moderation
By contrast, when people with obesity swallowed the sweetener, their insulin levels spiked a lot more compared with when they drank distilled water or when they only tasted the sweetener.
“While insulin responses to either tasting or swallowing the sucralose were similar in those of normal weight, those responses were very different in people with obesity. “Therefore, we hypothesize that some post-ingestive effects of sucralose may occur only in people with obesity.”
The researcher cautions, however, that different sweeteners have different chemical structures, so the findings of this study, regarding the “post-ingestive effects,” may apply exclusively to sucralose. Nevertheless, the effect of sweet taste alone may be more generalizable.
Intriguingly, and contrary to what the researchers expected, the study also found that merely tasting the sweetener had a metabolic effect, as well.
“Interestingly, we found that in both groups of people — those with obesity and those of normal weight — there was a reduction in insulin response to the glucose tolerance test when they just tasted sweetness before drinking the glucose solution.
The researchers acknowledge the limits of their results, saying, “What our data suggest is that there are mechanisms that we don’t understand clearly about how the human body regulates glucose, and the potential metabolic effects of tasting something sweet beyond providing a sense of pleasure.”
However, they stress the importance of eating sweet foods in moderation.
“Even though the sample population in our study was small, the findings add to a body of evidence that suggests sweetness should be consumed in moderation, regardless of the calories.
Will I get cancer from using artificial sweeteners like sucralose?
The first topic we delved into was that of the link between artificial sweeteners and cancer. This particular piece of research found that a chemical in a commonly used artificial sweetener may cause DNA damage.
The chemical in question was sucralose-6-acetate, a metabolite of the sweetener sucralose. The study findings showed that sucralose harms gut health and may lead to oxidative stress, inflammation, and DNA damage, and hence increase the risk of cancer.
Dr. Hilary Guite, our presenter, pointed out the most common food items that contain this sweetener: “It’s in chewing gum, salad dressings, barbecue sauces, sugar-free jams…”
One important nuance here was that this study was done on human blood cells. To see the same DNA-damaging effect in humans, an average human weighing 70 kilograms would have to consume 18 liters of sucralose-sweetened beverages daily.
How does diabetes affect children and teenagers?
Diabetes comes with various challenges, especially for young people. But, with early detection, children and teens can learn to manage diabetes and stay as healthy as possible. Early signs in children can include increased thirst and urination.
The National Diabetes Statistics Report 2020 states that around 210,000 children and teenagers under the age of 20 years in the United States have diagnosed diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is much more common in young people than type 2 diabetes. However, the rates of both types in young people are increasing.
In 2014–2015, doctors diagnosed type 1 diabetes in around 18,291 young people aged 10–19 years and type 2 diabetes in around 5,758 young people.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) report that, each year, rates of type 1 diabetes are rising by 1.8%, and rates of type 2 diabetes are rising by 4.8%.
Young people who develop diabetes have a higher risk of health challenges throughout their life.
This article will provide an overview of diabetes in children and teenagers, including the symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes are different conditions, but they both affect the body’s use of insulin. Although type 1 is more common in young people, both types can affect children and teenagers.
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes in children, previously called juvenile diabetes, occurs when the pancreas is unable to produce insulin.
Without insulin, sugar cannot travel from the blood into the cells, and high blood sugar levels can occur.
People can develop type 1 diabetes at any age, from early childhood to adulthood, but the average age at diagnosis is 13 years. An estimated 85% of all type 1 diagnoses take place in people aged under 20 years.
Treatment involves lifelong insulin use and blood sugar monitoring, as well as diet and exercise management, to help keep blood sugar levels within the target range.
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is less common in young children, but it can occur when insulin is not working correctly. Without enough insulin, glucose can accumulate in the bloodstream.
The chance of developing type 2 diabetes increases as people get older, but children can also develop it.
The rates of type 2 diabetes are increasing along with increases in childhood obesity. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report that obesity affected around 18.5% of children and adolescents aged 2–19 years in the U.S. in 2015–2016.
Over 75% of children with type 2 diabetes have a close relative who has it, either due to genetics or shared lifestyle habits. Having a parent or sibling with type 2 diabetes is linked with an increased risk.
Sometimes, the person will need medication. However, people can often manage type 2 diabetes by:
- changing the diet
- getting more exercise
- maintaining a moderate weight
The symptoms of diabetes are similar in children, teenagers, and adults. Some symptoms are common in both types of diabetes, but there are some differences to help tell them apart.
The symptoms of type 1 diabetes in children tend to develop rapidly over a few weeks. Type 2 diabetes symptoms develop more slowly. It may take months or years to receive a diagnosis.
Type 1 diabetes
The main symptoms of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents include:
- increased thirst and urination
- hunger
- weight loss
- fatigue
- irritability
- a fruity smell on the breath
- blurred vision
Weight loss is a common symptom before diagnosis. Yeast infections in females can also be a symptom of diabetes.
Some people will be experiencing diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) at the time of diagnosis. This occurs when the body begins to burn fat for energy due to a lack of insulin. This is a serious condition that requires treatment.
People may be able to get a diagnosis before DKA develops by recognizing the four main symptoms of type 1 diabetes.
Diabetes U.K. urge people to be aware of the “4 Ts” in children:
- Toilet: The child might be using the bathroom frequently, infants may be having heavier diapers, or bedwetting may be occurring after being dry for some time.
- Thirsty: The child may be drinking more fluids than usual but feeling unable to quench their thirst.
- Tired: The child may be feeling more tired than usual.
- Thinner: The child may be losing weight.
The video below provides more information on the 4 Ts:
Type 2 diabetes
The main symptoms of type 2 diabetes include:
- urinating more often, especially at night
- increased thirst
- tiredness
- unexplained weight loss
- itching around the genitals, possibly with a yeast infection
- slow healing of cuts or wounds
- blurred vision as a result of eye dryness
Another symptom of insulin resistance is the development of dark, velvety patches of skin, called acanthosis nigricans.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is another condition frequently associated with insulin resistance, though it is not a sign of it, per se.
Parents and caregivers should take their child to the doctor if they notice any of the above symptoms.
According to a 2012 survey from Diabetes U.K., only 9% of parents were able to identify the four main symptoms of type 1 diabetes in their children. By 2013, this figure had increased to 14%.
Some children do not receive a diagnosis until their symptoms are already severe. Receiving such a late diagnosis could prove fatal.
Do not miss the symptoms
Children and adolescents with diabetes usually experience four main symptoms, but many children will only have one or two. In some cases, they may show no symptoms at all.
If a child suddenly becomes more thirsty or tired or urinates more than usual, their parents may not consider diabetes a possibility.
This might also be the case for doctors, since diabetes is less common among very young children. They may attribute the symptoms to other, more common illnesses. For this reason, they may not diagnose diabetes straight away.
It is important to be aware of the possible signs and symptoms of diabetes in children in order to get a diagnosis and treatment plan as soon as possible.
One of the most serious consequences of undiagnosed type 1 diabetes is DKA. The sections below will look at this, and other complications, in more detail.
DKA
If a child does not receive treatment for type 1 diabetes, they may develop DKA. Type 2 diabetes can also lead to DKA, but this is rare.
DKA is a severe and life threatening condition that requires immediate treatment.
If insulin levels are very low, the body cannot use glucose for energy. Instead, it begins to break down fat for energy.
This leads to the production of chemicals called ketones, which can be toxic at high levels. A buildup of these chemicals causes DKA, wherein the body becomes acidic.
Early diagnosis and effective management of diabetes can prevent DKA, but this is not always possible. DKA is more common among children with an incorrect, and therefore delayed, diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.
One 2008 investigation found that among 335 children under the age of 17 years with new onset type 1 diabetes, the initial diagnosis was incorrect in more than 16%Trusted Source of cases.
Instead, they received the following diagnoses:
- respiratory system infection: 46.3%
- perineal candidiasis 16.6%
- gastroenteritis: 16.6%
- urinary tract infection: 11.1%
- stomatitis: 11.1%
- appendicitis: 3.7%
Type 2 diabetes complications
Without treatment, type 2 diabetes appears to progress faster in young people than in adults.
Younger people also seem to have a higher risk of complications, such as kidney and eye disease, earlier in life.
There is also a greater risk of high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels, which increase a person’s risk of blood vessel disease.
Type 2 diabetes in children often occurs with obesity, which may contribute to these higher risks. Obesity affects the body’s ability to use insulin, leading to abnormal blood sugar levels.
Because of this, early detection of type 2 diabetes and attention to managing overweight and obesity in younger people are crucial.
This may include encouraging children to follow a healthful diet and get plenty of exercise.
Any child with signs or symptoms of diabetes should see a doctor for screening. This may consist of a urine test to look for sugar in the urine or a finger-prick blood test to check the child’s glucose levels.
The National Institute for Health Care and Excellence recommend testing children for diabetes if they:
- have a strong family history of type 2 diabetes
- have obesity
- are of Black or Asian family origin
- show evidence of insulin resistance, such as acanthosis nigricans
The outcomes for children with type 1 or type 2 diabetes improve greatly with early detection.
It is not currently possible to prevent type 1 diabetes, but type 2 diabetes is largely preventable.
The following steps can help prevent type 2 diabetes in childhood:
- Maintain a moderate weight: Overweight increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as it increases the chance of insulin resistanceTrusted Source.
- Stay active: Keeping physically active reduces insulin resistance and helps manage blood pressure.
- Limit sugary foods and beverages: Consuming lots of foods that are high in sugar can lead to weight gain and problems with insulin function. Eating a balanced, nutrient-rich diet — with plenty of vitamins, fiber, and lean proteins — will lower the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes rates in childhood and adolescence are rising. Type 1 diabetes is much more common in young people than type 2 diabetes, but the rates of both are increasing.
In most cases, people can manage the symptoms of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes with a healthful diet, regular exercise, and medications.
When they control the condition well, people with diabetes can live full and healthy lives.
Why exercise is key to living a long and healthy life
What should we do in order to live healthier lives for longer? Research shows there are a few lifestyle interventions that can effectively prolong our life and health span. One of these is exercise, but what kind, and in what combinations, and why does it help add years to our lives?
Seemingly since times immemorial, humankind has been, metaphorically speaking, seeking the path that leads to the “Fountain of Youth” — that is ways to ensure a longer, healthier life.
And while we may not yet benefit of any “miracle” medicines or technologies to prolong our life spans well over the hundred-year mark, many recent studies have provided strong evidence in support of the notion that simple, achievable lifestyle changes can help us stay healthy for longer and decrease our risk of premature death.
Research presented at the American Heart Association’s Scientific Sessions 2023, for example, suggested that eight healthy habits can slow down biological aging by as much as 6 years.
These habits are related to diet, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding tobacco, maintaining good sleep hygiene, managing cholesterol, blood sugar, and blood pressure, and, no less importantly, staying physically active.
Dr. del Pozo Cruz is principal researcher in Applied Health Sciences at the University of Cadiz in Spain, and adjunct associate professor in the Department of Sports Science and Clinical Biomechanics at the University of Southern Denmark.
In collaboration with other researchers, Dr. del Pozo Cruz has conducted various studies exploring the link between different forms of exercise and the risk of death from different causes.
Dr. Brocklesby has gained fame under the nickname “Iron Gran,” as at the age of 72, she was the oldest British woman to complete an Ironman Triathlon. She is also founder and CEO of Silverfit, a not-for-profit organization promoting lifelong fitness.
What types of exercise lower death risk?
In a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine in August 2023, Dr. del Pozo Cruz and his colleagues analyzed data from 500,705 participants followed up for a median period of 10 years to see how different forms of exercise related to a person’s mortality risk.
The study looked at the effect of moderate aerobic physical activity, such as walking or gentle cycling, vigorous aerobic physical activity, such as running, and muscle-strengthening activity, like weight lifting.
Its findings indicated that a balanced combination of all of these forms of exercise worked best for reducing mortality risk.
More specifically, around 75 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise, plus more than 150 minutes of vigorous exercise, alongside at least a couple of strength training sessions per week were associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality.
When it came to reducing the risk of death linked to cardiovascular disease specifically, Dr. del Pozo Cruz and his collaborators suggested combining a minimum of 150–225 minutes of moderate physical activity with around 75 minutes of vigorous exercise, and two or more strength training sessions per week.
Dr. Brocklesby, who goes by “Eddie,” is herself an example of the importance of combining different forms of exercise. Indeed, training and participating in a triathlon — which is an endurance multisport race where participants compete in swimming, cycling, and running — involves achieving a balanced “diet” of moderate and vigorous exercise, as well as strength training.
How little exercise is enough?
But what about people who are not nearly as athletic? What is the minimum “amount” of exercise that could help fend off some of the conditions that pose the highest threat to health?
Dr. del Pozo Cruz and his team may also have found an answer to this question. In December 2022, they published the findings to a previous study in the European Heart Journal.
This research suggested that engaging in vigorous exercise for only 2 minutes a day could help slash the risk of death related to cancer or cardiovascular events.
The researchers found that study participants who never engaged in vigorous exercise had a 4% risk of dying within 5 years, but introducing less than 10 minutes of vigorous activity weekly halved this risk. Moreover, their risk of death halved again for those who engaged in at least 60 minutes of exercise per week.
Is any physical activity good?
In our podcast, Dr. del Pozo Cruz emphasized that almost any amount of any form of exercise is better than none, a point reinforced by a new study arguing that any activity at all is better for heart health than a sedentary lifestyle.
However, he also cautioned that physical activity related to chores or to one’s job, as opposed to exercise in a leisure context, may sometimes do more harm than good.
Once again, his idea is supported by recently published research, which found a link between physically demanding occupations and a higher risk of cognitive impairment.
Some of the most common occupations linked to intensive physical activity cited in this research were in nursing and care, retail, and farming, where individuals are on their feet a lot, and often having to deal with stressful situations.
So while all forms of exercise can be good for health, strenuous or intensive physical activity in a work environment could end up compounding the risk of various health conditions.
And even exercise for leisure can affect aspects of physical health — such as joint integrity — particularly later in life. In our podcast, both Dr. del Pozo Cruz and Eddie emphasized the importance of consulting a trusted healthcare provider, who can advise on the best forms of exercise to engage in on an individual basis.
To find out more about how and why different forms of exercise can support longevity, and to hear the story of how Edwina became “Iron Gran,” listen to our podcast episode in full below or on your preferred streaming platform.
Swapping meat for plant-based foods may lower diabetes and heart disease ris
Can going plant-based help slash metabolic and cardiovascular risk?
- Analyzing over 30 studies, German researchers found that swapping meats for plant-based alternatives may drastically reduce risks of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and all-cause mortality.
- Evidence showed that replacing 50 grams (1.8 ounces) of processed meat with plant-based foods on a daily basis lowered cardiovascular disease risk by 25%.
- Substituting processed meats was associated with a 21% lower risk of death from any cause.
The Western diet is replete with red and processed meats and other animal products. Experts worry that this eating pattern strains natural resources, triggers negative climate change, and contributes to an array of noncommunicable diseases.
The environmental and health burdens associated with the Western diet are increasingly supporting the case for promoting plant-based dietary alternatives.
Some studies have suggested that plant-based foods may help lower the risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, and overall mortality.
So far, however, research has not considered the full cardiometabolic implications of switching out meats for plants in a systematic review and meta-analysis.
To address this deficit, researchers from institutions in Germany collaborated on a paper exploring the topic. Their systematic review and meta-analysis article was published in BMC MedicineTrusted Source.
“Our findings indicate that a shift from animal-based (e.g., red and processed meat, eggs, dairy, poultry, butter) to plant-based (e.g., nuts, legumes, whole grains, olive oil) foods is beneficially associated with cardiometabolic health and all-cause mortality,” the authors reported.
First review of its kind
The research team ran a systematic literature search on MEDLINE, Embase, and Web of Science.
They included studies that used substitution analyses of animal-based food with plant-based foods. The studies consulted also discussed health outcomes such as cardiovascular disease, coronary heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and all-cause mortality.
Furthermore, the studies were prospective observational studies conducted among the general healthy population.
Each study underwent a risk of bias assessment with the Risk of Bias in Non-Randomized Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I)Trusted Source tool. The team evaluated the certainty of evidence for each association using the Grading of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations (GRADE)Trusted Source protocol.
The research team narrowed their search down from 1,216 to 32 studies for final inclusion in their analyses. Hand searching yielded another five studies, for a total of 37 meta-analyses.
According to the authors, their work “is the first systematic review and meta-analysis that summarized the associations between the substitution of animal-based with plant-based foods with a wide range of cardiometabolic outcomes, such as cardiovascular disease mortality; incidence of [cardiovascular disease, coronary heart disease, and type 2 diabetes]; diabetes mortality, and all-cause mortality.”
Swapping animal- for plant-based foods for health
The researchers observed a “moderate certainty of evidence” that replacing one daily egg with nuts correlated with lower cardiovascular disease mortality. Substituting butter with olive oil yielded similar results.
Switching 50 grams (g) of processed meat with 28 g of nuts daily was associated with a lower coronary heart disease incidence. Replacing poultry or seafood with nuts or legumes was not.
There was only a low certainty of evidence for associations of reduced coronary heart disease risk with replacing red meat with nuts or legumes.
Replacing butter with olive oil, red meat with nuts, or one egg daily with nuts, was inversely associated with type 2 diabetes frequency, the researchers also found.
Finally, the research team noticed a moderate certainty of evidence for a lower risk of all-cause mortality when switching red meat with nuts or whole grains. Replacing processed meat with nuts or legumes, or unprocessed red meat with nuts also reduced this risk.
Substituting dairy or one egg daily with nuts or legumes, or butter with olive oil, was associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality.
These findings agree with a prior review suggesting that replacing red meat with plant-based foods lowered the risk of coronary heart disease and all-cause mortality.
This work also supports other studies tying higher meat consumption with coronary heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and all-cause mortality.
Review highlights ‘vital’ role of plant-based foods in health
The present study was the first meta-analysis of its kind. Validated food frequency questionnaires were used to collect dietary information. The mean follow-up duration among the cohorts was 19 years.
Most of the studies included males and females, with a few gender-specific exceptions.
Medical News Today discussed this study with Eva De Angelis, a registered dietitian nutritionist. She was not involved in the research.
De Angelis considered the investigation “quite a fascinating systematic review that further highlights the vital role plant foods can have on our overall health, and how too many animal foods can have the opposite effect.”
She was impressed that the study used many diverse prospective studies, which “provide a higher quality of evidence.”
The focus on multiple health outcomes was another strength, Ms. De Angelis told MNT.
How does the review fall short?
Nevertheless, the research team also acknowledged several limitations to their study, stressing that their “findings should be interpreted with caution.”
Many of the studies analyzed used theoretical food substitutions. Moreover, portion sizes differed among studies, resulting in unequal comparisons of dietary substitutes.
Using only prospective observational studies presented the potential for residual confounding and measurement inaccuracies.
Furthermore, the limited number of studies in the final analysis did not allow for subgroup assessments. For instance, dairy products were assessed as one group. The authors noted that “dairy includes a wide range of different products (e.g., milk, yogurt, cheese) with different associations with cardiometabolic outcomes.”
De Angelis commented: “Among the weaknesses, I would mention that the information only allows us to make associations, and not causality, because many of the analyzed studies were observational. This means we don’t know for sure if any other factors may have been involved in the outcomes.”
The review authors felt that more research was needed to support the existing evidence. They expressed their hope that future work would explore new interconnections and highlight meat and dairy replacements.
Better dietary choices for our bodies and the planet?
MNT also discussed this study with registered dietitian nutritionist Sara Chatfield. She was not involved in the research.
Chatfield pointed out that transitioning to more plant-based foods can reap significant benefits to the planet, because animal production is so resource- and land-intensive.
In fact, both of the nutritionists interviewed by MNT agreed that focusing more on whole plant foods can only help the Earth and its inhabitants.
Chatfield referred to research suggesting that shifting to plant-based dietary patterns could reduce diet-related land useTrusted Source by 76% and greenhouse gas emissions by 49%.
De Angelis shared a similar view, saying that:
“There is no denying that following a mainly plant-based diet has been proven beneficial not only for our overall health but also for the planet as we reduce our carbon footprint by choosing such foods.”
Both nutritionists cautioned, however, that a fully plant-based diet may not be the best option for some, depending on an individual’s health conditions, preferences, and food accessibility.
Still, De Angelis emphasized that “trying to add more plant foods to your diet can be an easy and simple step for better health.”
What is depression and what can I do about it?
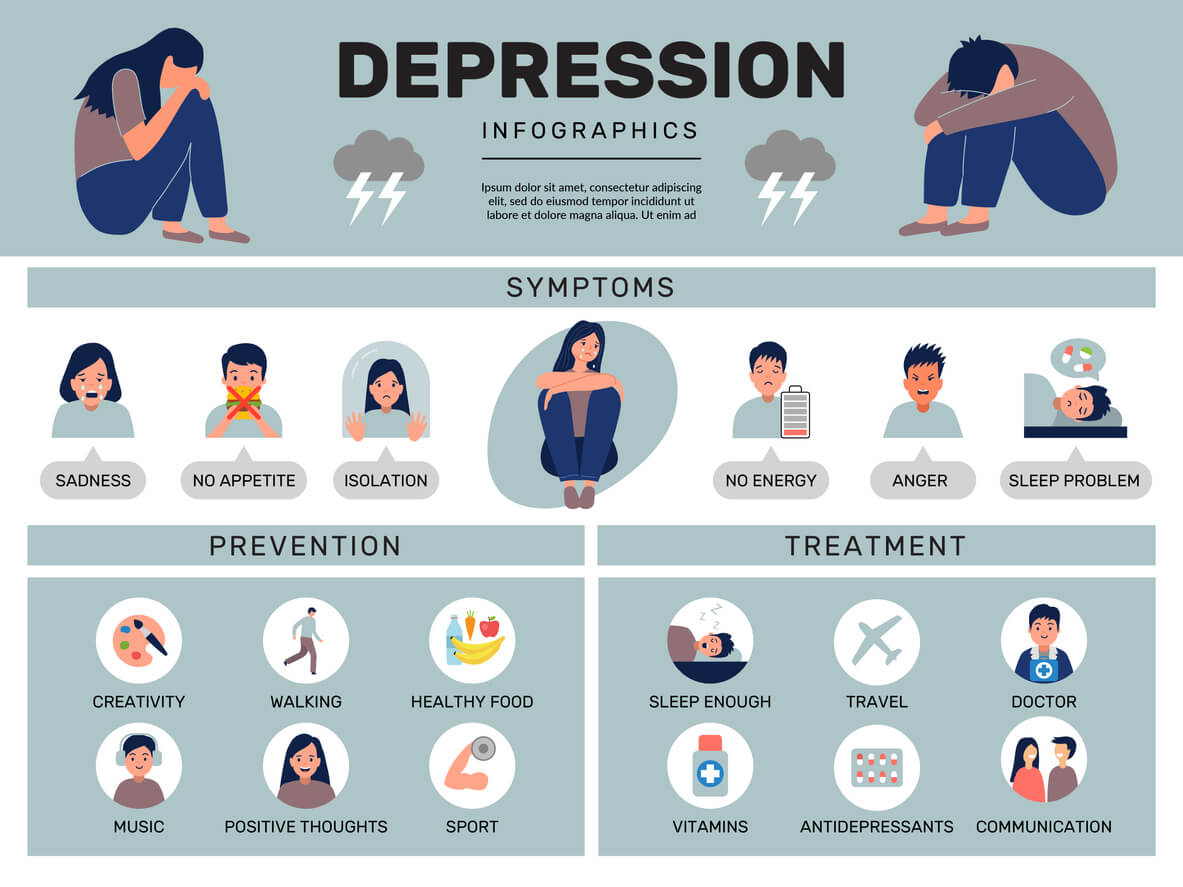
Depression is a mental health condition that causes a chronic feeling of emptiness, sadness, or inability to feel pleasure that may appear to happen for no clear reason.
Depression is the leading cause of disability worldwide, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
It can undermine a person’s relationships, make working and maintaining good health very difficult, and in severe cases, may lead to suicide. In fact, depression contributes to nearly 40,000 suicides in the United States each year.
It can affect adults, adolescents, and children. This article examines what depression is and what causes it, as well as types of depression, treatment, and more.
Depression is a mood disorder that causes persistent feelings of sadness, emptiness, and loss of joy. It is different from the mood fluctuations that people regularly experience as a part of life.
Major life events, such as bereavement or the loss of a job, can trigger depression. But depression is distinct from the negative feelings a person may temporarily have in response to a difficult life event.
Depression often persists in spite of a change of circumstances and causes feelings that are intense, chronic, and not proportional to a person’s circumstances.
It is an ongoing problem, not a passing one. While there are different types of depression, the most common one is major depressive disorder. It consists of episodes during which the symptoms last for at least two weeks.
Depression can last for several weeks, months, or years. For many people, it is a chronic illness that gets better and then relapses.
While there is no cure for depression, there are effective treatments that help with recovery. The earlier that treatment starts, the more successful it may be. Some people may never experience depression again after a single period of it. Others will continue to have relapses.
Many people experiencing depression recover after a treatment plan. Even with effective treatment, however, a relapse may occur. About half of people do not initially respond to treatment.
To prevent relapse, people who take medication for depression should continue with treatment — even after symptoms improve or go away — for as long as their doctor advises.
Find tips to help prevent depression from returning here.
Depression can cause a range of psychological and physical symptoms, including
- persistent depressed mood
- loss of interest or pleasure in hobbies and activities
- changes in appetite and body weight
- unusually slow or agitated movements
- decreased energy or fatigue
- difficulty sleeping or oversleeping
- excessive feelings of guilt or worthlessness
- difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- thoughts of death or suicide, or suicide attempts
If a person experiences five Trusted Sourceor more of these symptoms during the same 2-week period, a doctor may diagnose them with depression.
Depression may also cause other symptoms, including irritability, restlessness, chronic pain, headaches, and digestive issues.
There are several forms of depression. Below are some of the most common types.
Major depression
A person living with major depression experiences a constant state of sadness. They may lose interest in activities they used to enjoy.
Treatment usually involves medication and psychotherapy.
Persistent depressive disorder
Also known as dysthymia, persistent depressive disorder causes symptoms that last for at least 2 years.
A person living with this disorder may have episodes of major depression as well as milder symptoms that do not meet the criteria for major depressive disorder.
Postpartum depression
After giving birth, some people experience a brief period of sadness or heightened emotions that some people call the “baby blues.” This usually goes away in a few days to a few weeks.
Postpartum depression, or postnatal depression, is more severe.
There is no single cause for this type of depression, and it can persist for months or years. Anyone who experiences ongoing depression after delivery should seek medical attention.
Major depressive disorder with seasonal pattern
Previously known as seasonal affective disorder (SAD), this type of depression usually occurs during the winter and fall months, when there is less daylight. Less commonly, it may follow other seasonal patterns.
It lifts during the rest of the year and in response to light therapy.
This condition seems to particularly affect people who live in countries with long or severe winters.
The medical community does not fully understand the causes of depression. There are many possible causes, and sometimes, various factors combine to trigger symptoms.
Factors that are likely to play a role include:
- genetic features
- changes in the brain’s neurotransmitter levels
- environmental factors such as exposure to trauma or lack of social support
- psychological and social factors
- additional conditions, such as bipolar disorder
Interactions between various factors can increase the risk of depression. For instance, a person with a family history or a genetic risk of depression may experience symptoms of depression following a traumatic event.
The symptoms of depression can include:
- a depressed mood
- reduced interest or pleasure in activities that a person previously enjoyed
- a loss of sexual desire
- changes in appetite
- unintentional weight loss or gain
- sleeping too much or too little
- agitation, restlessness, and pacing up and down
- slowed movement and speech
- fatigue or loss of energy
- feelings of worthlessness or guilt
- difficulty thinking, concentrating, or making decisions
- recurrent thoughts of death or suicide, or an attempt at suicide
Find out more about recognizing the hidden signs of depression here.
In females
Depression is nearly twice as common in females than males, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Researchers do not know why depression appears to be more common in females. However, a 2021 study proposes that the difference may be due to disparities in reporting. Researchers found that females were more likely than males to report and seek treatment for depression symptoms.
Some research suggests that exposure to gender discrimination increases the risk of depression.
Also, some types of depression are unique to females, such as postpartum depression and premenstrual dysphoric disorder.
In males
According to data from the National Health and Nutrition study, which relies on self-reports of mental health symptoms, 5.5% of males report depression symptoms in a given 2-week period, compared with 10.4% of females.
Males with depression are more likely than females to drink alcohol in excess, display anger, and engage in risk-taking as a result of the disorder.
Other symptoms of depression in males may include:
- avoiding family and social situations
- working without a break
- having difficulty keeping up with work and family responsibilities
- displaying abusive or controlling behavior in relationships
Learn more about the symptoms of depression in men.
In college students
Time at college can be stressful, and a person may be dealing with other lifestyles, cultures, and experiences for the first time.
Some students have difficulty coping with these changes, and they may develop depression, anxiety, or both as a result.
Symptoms of depression in college students may include:
- difficulty concentrating on schoolwork
- insomnia
- sleeping too much
- a decrease or increase in appetite
- avoiding social situations and activities that they used to enjoy
In teens
Physical changes, peer pressure, and other factors can contribute to depression in teenagers.
They may experience some of the following symptoms:
- feeling irritable
- restlessness, such as an inability to sit still
- withdrawing from friends and family
- difficulty concentrating on schoolwork
- feeling guilty, helpless, or worthless
In children
The CDC estimate that, in the U.S., 4.4% of children and teenagers aged 3–17 have a diagnosis of depression. This figure has risen in recent years.
Depression in children can make schoolwork and social activities challenging. They may experience symptoms such as:
- crying
- low energy
- clinginess
- defiant behavior
- vocal outbursts
Younger children may have difficulty expressing how they feel in words. This can make it harder for them to explain their feelings of sadness.
Learn more about mental health in trans people here.
In historically marginalized groups
Research shows that the prevalence of major depression among African Americans has been around 10.4%, compared with 17.9% among people who are white.
However, 56% of African Americans experience depression more chronically, compared with 38.6% of people who are white. This implies that though fewer African Americans may experience depression, those who do may experience it for longer. In addition, less than half of these African Americans have sought treatment.
Other research indicates that African Americans may have depression less frequently than non-Hispanic people who are white, but this may be due to the fact that many African Americans often do not have a proper diagnosis.
Triggers are emotional, psychological, or physical events or circumstances that can cause depression symptoms to appear or return.
These are some of the most common triggers:
- stressful life events, such as loss, family conflicts, and changes in relationships
- incomplete recovery after having stopped depression treatment too soon
- medical conditions, especially a medical crisis such as a new diagnosis or a chronic illness such as heart disease or diabetes
Find out more about depression triggers here.
Some people have a higher risk of depression than others.
Risk factors include:
- experiencing certain life events, such as bereavement, work issues, changes in relationships, financial problems, and medical concerns
- experiencing acute stress
- having a lack of successful coping strategies
- having a close relative with depression
- using some prescription drugs, such as corticosteroids, certain beta-blockers, and interferon
- using recreational drugs, such as alcohol or amphetamines
- having sustained a head injury
- having a neurodegenerative disease such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s
- having had a previous episode of major depression
- having a chronic condition, such as diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or cardiovascular disease
- living with chronic pain
- lacking social support
Depression can also occur as a symptom or comorbidity with another mental health condition. Examples include:
Psychotic depression
Psychosis can involve delusions, such as false beliefs and a detachment from reality. It can also involve hallucinations — sensing things that do not exist.
Some people experience depression with psychosis. A person living with psychosis, which is a serious psychiatric illness, may experience depression as a result.
Alternatively, a person living with depression may have a severe form of the condition that also includes psychosis symptoms.
Bipolar disorder
Depression is a common symptom of bipolar disorder. People with bipolar disorder experience periods of depression that may last weeks. They also experience periods of mania, which is an elevated mood that may cause a person to feel very happy, aggressive, or out of control.
What does bipolar disorder involve, and what types are there? Find out here.
Depression is treatable, though the treatment may depend on the exact type a person is living with.
However, about 30.9% of people do not respond to treatment or respond poorly. About 4 in 10 people achieve remission of their symptoms within 12 months, but depression can come back.
Managing symptoms usually involves three components:
- Support: This can range from discussing practical solutions and possible causes to educating family members.
- Psychotherapy: Also known as talking therapy, some options include one-to-one counseling and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT).
- Drug treatment: A doctor may prescribe antidepressants.
Medication
Antidepressants can help treat moderate to severe depression. Several classes of antidepressants are available:
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
- selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
- atypical antidepressants
- tricyclic antidepressants
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
Each class acts on a different neurotransmitter or combination of neurotransmitters.
A person should only take these medications as their doctor prescribes. Some drugs can take a while to have an impact. By stopping taking the drug, a person may not experience the benefits that it can offer.
Some people stop taking medication after symptoms improve, but this can lead to a relapse.
A person should raise any concerns about antidepressants with a doctor, including any intention to stop taking the medication.
Learn more about antidepressants and how they can help here.
Medication side effects
SSRIs and SNRIs can have side effects. A person may experience:
- nausea
- constipation
- diarrhea
- low blood sugar
- weight loss or weight gain
- a rash
- sexual dysfunction
Find out more about the possible side effects of antidepressants here.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires manufacturers to put a “black box” warning on antidepressant bottles.
The warning indicates that, among other risks, these medications may increase suicidal thoughts or actions in some children, teenagers, and young adults within the first few months of treatment. While there is an increase in risk, the absolute risk remains low.
Natural remedies
Some people use natural remedies, such as herbal medicines, to treat mild to moderate depression.
However, since the FDA does not monitor herbal remedies, manufacturers may not be truthful about the quality of these products. They may not be safe or effective.
In a 2018 systematic review of herbal remedies for depression, 45% of studies reported positive results from herbal treatments, including fewer side effects than standard antidepressants.
The following are some of the more popular herbs and plants that people use to treat depression:
- St. John’s wort: This is not suitable for people who are or may be living with bipolar disorder. Learn more here.
- Ginseng: Practitioners of traditional medication may use this to improve mental clarity and reduce stress. Find out more about ginseng here.
- Chamomile: This contains flavonoids that can have an antidepressant effect. For more information about chamomile, click here.
- Lavender: This may help reduce anxiety and insomnia. Learn more about lavender here.
It is essential for a person to speak with a doctor before using any type of herbal remedy or supplement to treat depression. Some herbs can interfere with the action of drugs or otherwise make symptoms worse.
Supplements
A person may take the herbs above as supplements to treat symptoms of mild to moderate depression. Other types of supplements can also help treat these symptoms.
It is important to remember that the FDA does not monitor supplements to ensure that they are effective or safe.
Nonherbal supplements that may help treat depression include S-adenosyl methionine (SAMe) — a synthetic form of a natural chemical in the body. They also include 5-hydroxytryptophan, which can help to boost serotonin, the neurotransmitter in the brain that affects a person’s mood.
Some research has suggested that SAMe may be as helpful as the prescription antidepressants imipramine and escitalopram, but more investigation is necessary.
Learn more about how herbs and supplements may help relieve depression here.
Food and diet
Some research suggests that eating a lot of sugary or processed foods can lead to various physical health problems and poor mental health. Results of a 2019 study suggest that a diet that includes many of these types of food can affect the mental health of young adults.
The study also found that eating more of the following foods helped reduce depression symptoms:
- fruit
- vegetables
- fish
- olive oil
Can other foods worsen or improve depression symptoms? Find out here.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, or talking therapies, for depression include CBT, interpersonal psychotherapy, and problem-solving treatment.
For some forms of depression, psychotherapy is usually the first-line treatment, while some people respond better to a combination of psychotherapy and medications.
CBT and interpersonal psychotherapy are the two main types of psychotherapy for depression. A person may have CBT in individual sessions with a therapist, in groups, over the telephone, or online.
CBT focuses on helping a person identify the connection between their thoughts, behaviors, and feelings. They then work steadily to change harmful thoughts and behaviors.
Interpersonal therapy aims to help people identify:
- emotional problems that affect relationships and communication
- how these issues also affect their mood
- how to improve relationships and better manage emotions
Exercise
Aerobic exercise raises endorphin levels and stimulates neurotransmitters, potentially easing depression and anxiety. A 2019 paper states that exercise may be especially helpful with treatment-resistant depression.
Exercise offers the greatest benefits when a person combines it with standard treatments, such as antidepressants and psychotherapy.
Brain stimulation therapies
Brain stimulation therapies are another treatment option. For example, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation sends magnetic pulses to the brain, and this may help treat major depression.
If depression does not respond to drug treatment, a person may benefit from electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Doctors do not fully understand how ECT works.
During the procedure, a person is asleep, and a doctor uses electricity to induce a seizure. This may help “reset” the brain, correcting problems with neurotransmitters or other issues that cause depression.
If a person suspects that they have symptoms of depression, they should seek professional help from a doctor or mental health specialist.
A qualified health professional can rule out various causes, ensure an accurate diagnosis, and provide safe and effective treatment.
They will ask questions about symptoms, such as how long they have been present. A doctor may also conduct an examination to check for physical causes and order a blood test to rule out other health conditions.
What is the difference between situational and clinical depression? Find out here.
Tests
Mental health professionals often ask people to complete questionnaires to help assess the severity of their depression.
The Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, for example, has 21 questions. The scores indicate the severity of depression among people who already have a diagnosis.
The Beck Depression Inventory is another questionnaire that helps mental health professionals measure a person’s symptoms.
National hotlines provide free, confidential assistance from trained professionals 24 hours a day. They may benefit anyone with depression who wants or needs to talk about their feelings.
Some of the support hotlines available include:
- Samaritans: This nonprofit organization offers emotional support to anyone who has feelings of depression or loneliness or who is considering suicide. Call or text 877-870-4673 (HOPE).
- National Suicide Prevention Lifeline: Call 1-800-273- 8255 (TALK) to speak with someone from this national network of local crisis centers.
- Lifeline Chat: This is an online chat service of the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline.
- Postpartum Support International: Call 1-800-944-4773. This organization helps people struggling with postpartum depression, as well as other mental health issues that are related to pregnancy, birth, and new parenthood.
A person with a parent or sibling who has depression is about three times more likely than other people to develop the condition.
However, many people with depression have no family history of it.
A recent study suggests that susceptibility to depression may not result from genetic variation. The researchers acknowledge that while people can inherit depression, many other issues also influence its development.
Learn more about whether depression has a genetic link here.
Depression is the leading cause of disability around the world, according to the WHO.
In the U.S., the Social Security Administration considers depressive, bipolar, and related disorders to be disabilities. If a person’s depression prevents them from working, they may qualify for social security disability insurance benefits.
The person must have worked long enough and recently enough to qualify for disability benefits. For more information, visit the administration’s website.
According to the CDC, about 11% of physician office visits note depression on the medical record. The figure is similar for emergency department visits.
Also according to the CDC, 4.4% of children and adolescents between the ages of 3 and 17 years — about 2.7 million people in the U.S. — have a diagnosis of depression.
The CDC also note that 4.7% of American adults have regular feelings of depression.
Here are some common questions about depression.
What does depression do to the brain?
Depression can lead to changes in levels of neurotransmitters, which are molecules that transmit messages between nerve cells. In the long run, it may also cause physical changes to the brain, including reductions in grey matter volume and increased inflammation.
Does depression change your personality?
Research has turned up mixed results about whether or not depression can actually change a person’s personality.
However, according to one review of 10 studies, depressive symptoms may be associated with changes in several specific aspects of personality — including extraversion, neuroticism, and agreeableness — which could be temporary or persistent.
Does depression affect your thinking?
Depression can alter concentration and decision-making. It may also impair attention and cause issues with information processing and memory.
Depression is a serious, chronic medical condition that can affect every aspect of a person’s life. When it causes suicidal thoughts, it can be fatal.
People cannot think their way out of depression. Depression is not a personal failing or a sign of weakness. It is treatable, and seeking treatment early may increase the chances of recovery.
Because depression can be challenging to treat, it is important for a person to see a doctor with expertise in depression and to be willing to try several different treatments. Often, a combination of therapy and medication offers the best results.