What is the difference between cold and flu?
Both flu (influenza) and cold are caused by viruses, and they can have similar symptoms. So how do we know if a person has the flu or a bad cold? In this article, we explain the differences.
Cold and influenza are the most common illnesses in humans.
. Every year, 5-20 percent of the population of America develop flu symptoms.
The main difference between cold and flu is that, generally, symptoms of the flu are usually a lot more severe.
Each year, more than 200,000 people are hospitalized because of flu complications; flu is responsible for around 23,600 deaths every year.
Fast facts on colds vs. flu:
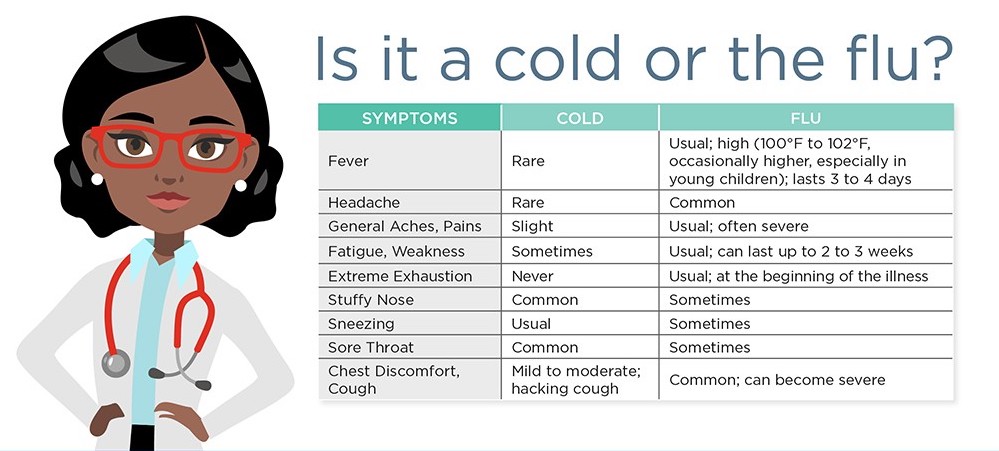
- Colds and flu share many of the same symptoms; the major difference being flu is often worse, and accompanied by a high fever.
- According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the average adult will have 2-3 colds every year.
- The rhinovirus is the most common cause of cold.
The difference between cold and flu
Cold and flu are caused by different viruses, and, in general, the symptoms of flu are worse. Also, there are less likely to be serious complications from cold, such as pneumonia and bacterial infections.
The main difference between cold and flu symptoms is that flu more commonly includes fever; the fever can be 100 degrees Fahrenheit or higher and last for 3-5 days.
The extreme fatigue associated with flu can persist for weeks. Cold symptoms are generally milder and last about 1 week.
Also, runny nose or nasal congestion is more common with cold than flu.
Vomiting is another key difference; vomiting is not normally associated with the common cold but can be present in flu.
Although the differences above are generally true, without conducting special tests, it is impossible to know for sure whether it is flu or cold. For instance, it is possible to have flu without fever.
What is a cold?
Almost everybody is familiar with the sensation of having a cold. Colds affect both warm and cool climates equally, and the average person will have had many colds from infancy all the way until later life.
Symptoms include a runny nose, sore throat, coughing and sneezing, watery eyes, a headache, and body aches. There is no cure, except for resting and drinking plenty of fluids, but the cold should pass within 7-10 days.
There is normally no need to visit a doctor, but a person with a weakened immune system is more prone to developing pneumonia as a complication
To avoid catching or spreading a cold, people should wash their hands regularly and make sure they sneeze into a tissue or handkerchief, or into their elbow. This is the most hygienic as it stops the spread of germs, which cannot live on clothing or surfaces like they can on skin.
What is flu?
There are three types of flu virus, influenza A, influenza B, and influenza C. Types A and B are the ones that cause seasonal epidemics. One of the key symptoms of flu is feeling feverish or having a temperature of 100 degrees Fahrenheit or above. However, not everyone with the flu will have a fever.
Other symptoms include:
- headaches or body aches
- vomiting, nausea, and possibly diarrhea, especially in children
- a sore throat and a cough
- fatigue
- chills and shivering
- a congested or runny nose
A common cold is less likely to cause a high fever. With a cold, symptoms such as a runny nose or throat irritation will normally improve within a few days.
How to treat flu
The CDC note that the majority of people who have the flu do not need medical attention. Most can remain at home and avoid contact with other people to prevent the disease from spreading. However, the following treatments are available:
- Over-the-counter medications – these can reduce fever. Tylenol can help people with flu feel more comfortable while they recover. Tylenol is also available to purchase online.
- Prescription antiviral flu drugs – these are also available from a physician. They are for people who are at high risk of serious complications and are not normally necessary for effective treatment. They can only be given within a certain amount of time from symptom onset.
- Home remedies – to alleviate symptoms, home remedies such as steam inhalation, nourishing foods like chicken soup, keeping warm, and other comfort measures can be used.
A physician will be able to decide if antivirals are needed. People who tend to be at greater risk include infants under the age of 2, people aged 65 years and older, and pregnant women.
Emergency warning signs for flu
Patients should seek medical help if they notice any of the emergency warning signs.
Warning signs in infants include difficulty breathing, having no appetite, and not producing tears when they cry, or having fewer wet diapers than usual.
Severe symptoms in older children include:
- breathing problems
- bluish skin color
- not drinking enough fluids
- not waking up or interacting
- being so irritable that they do not want to be held
- fever with a rash
If flu-like symptoms improve but then return with fever and a worse cough, the parent should consult a physician.
Anti-flu vaccines and other types of protection
The best way to protect against the flu is by having an annual vaccination, as this helps the body to build up the immune system so that it can fight off the virus more quickly.
The flu vaccine is recommended during pregnancy as it has been proven safe. If flu occurs during pregnancy, it can have serious complications for the unborn child and the mother.